

The law of reflection is very simple: The angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence.
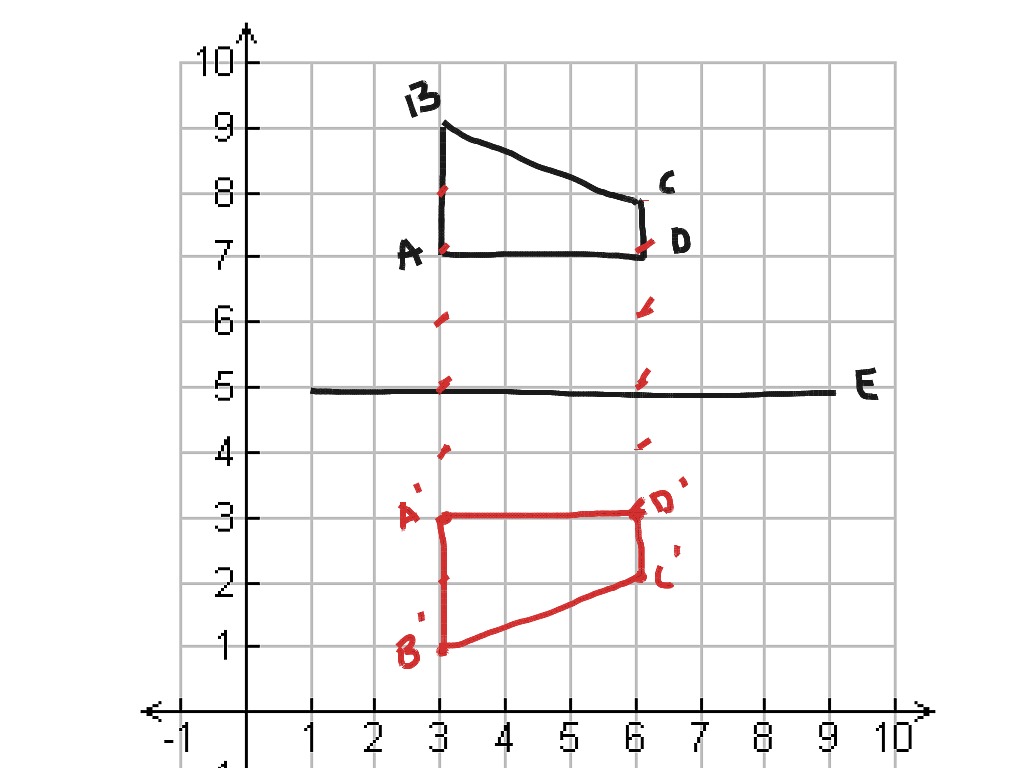
Only the observer at a particular angle will see the reflected light. Who can see who angle of reflection?Ī mirror illuminated by many parallel rays reflects them in only one direction, since its surface is very smooth. Specular reflection is defined as light reflected from a smooth surface at a definite angle, whereas diffuse reflection is produced by rough surfaces that tend to reflect light in all directions (as illustrated in Figure 3). The reflection of light can be roughly categorized into two types of reflection. (ii) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Laws of reflection are: (i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal ray at the point of incidence, lie in the same plane. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence-θr = θi. Both angles are measured with respect to the normal to the mirror. The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the mirror, all lie in the same plane. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal. The laws of reflection are as follows: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane. The angle α is called the angle of incidence and the angle β is called the angle of reflection. The law of reflection says that the angle between the incoming ray and the mirror is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the mirror. 6 What is the formula for the law of refraction?.5 What is the law of reflection in physics?.1 What is the law of reflection in math?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
